Condition
Learn about condition and how to implement it effectively.
Condition (Agentflow Node)
The Condition node within Agentflow allows you to introduce conditional logic into your AI workflows, enabling dynamic branching based on specific criteria. This is crucial for creating intelligent workflows that can adapt their behavior based on data, user input, or other runtime variables.
Purpose
The Condition node evaluates one or more conditions and directs the workflow along different paths (outputs) based on whether these conditions are met. It supports various comparison types (string, number, boolean) and operations, making it highly flexible for decision-making.
Appearance on Canvas
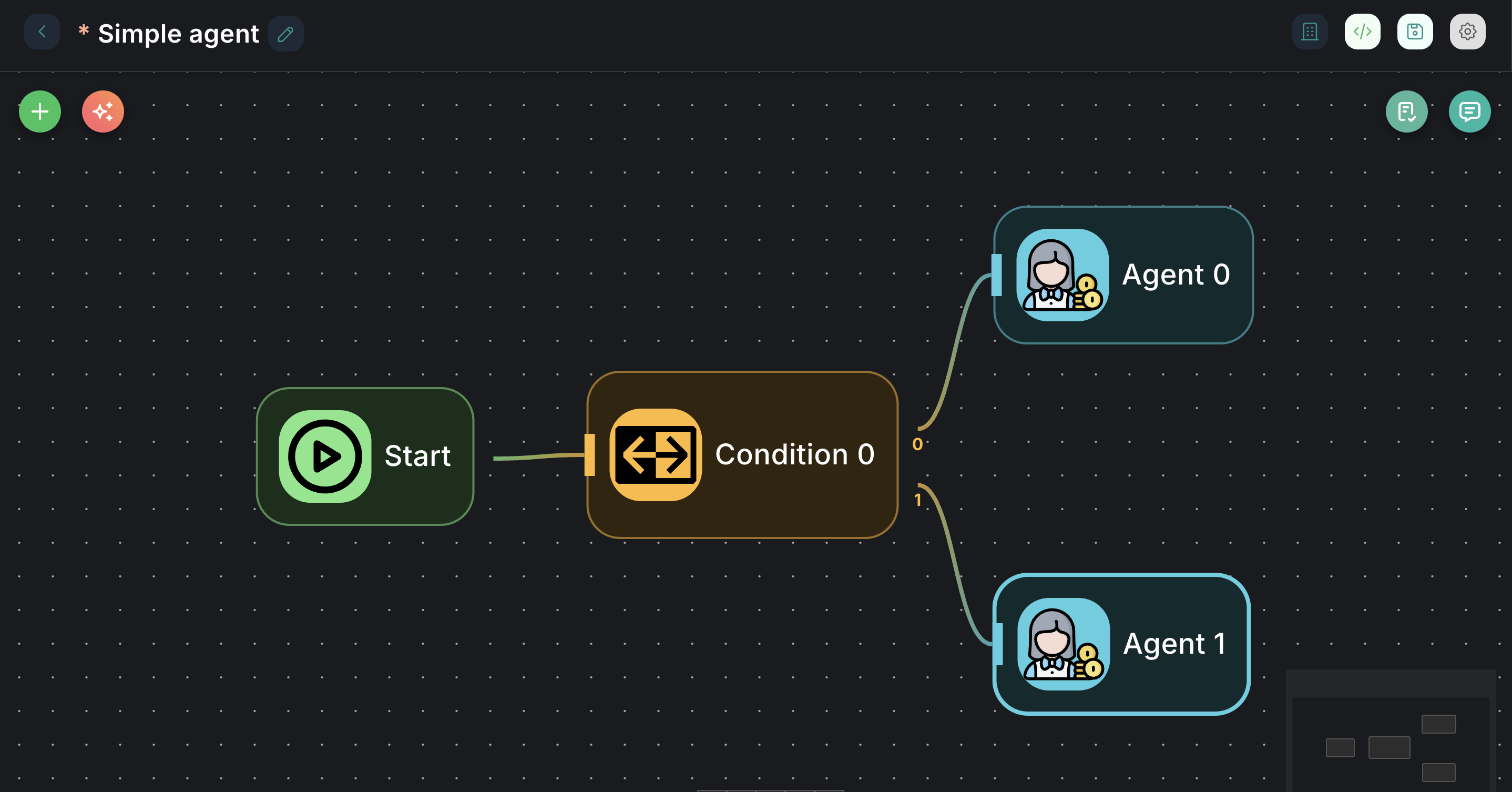
Configuration Parameters
The Condition node's primary configuration is the Conditions array, where you define the rules for branching.
1. Conditions (Required)
- Label: Conditions
- Type:
arrayof objects - Description: A list of conditions to be evaluated. The workflow will proceed down the output corresponding to the first condition that evaluates to
true. If no conditions are met, it will proceed down the "Else" path.
Each individual condition within the array has the following properties:
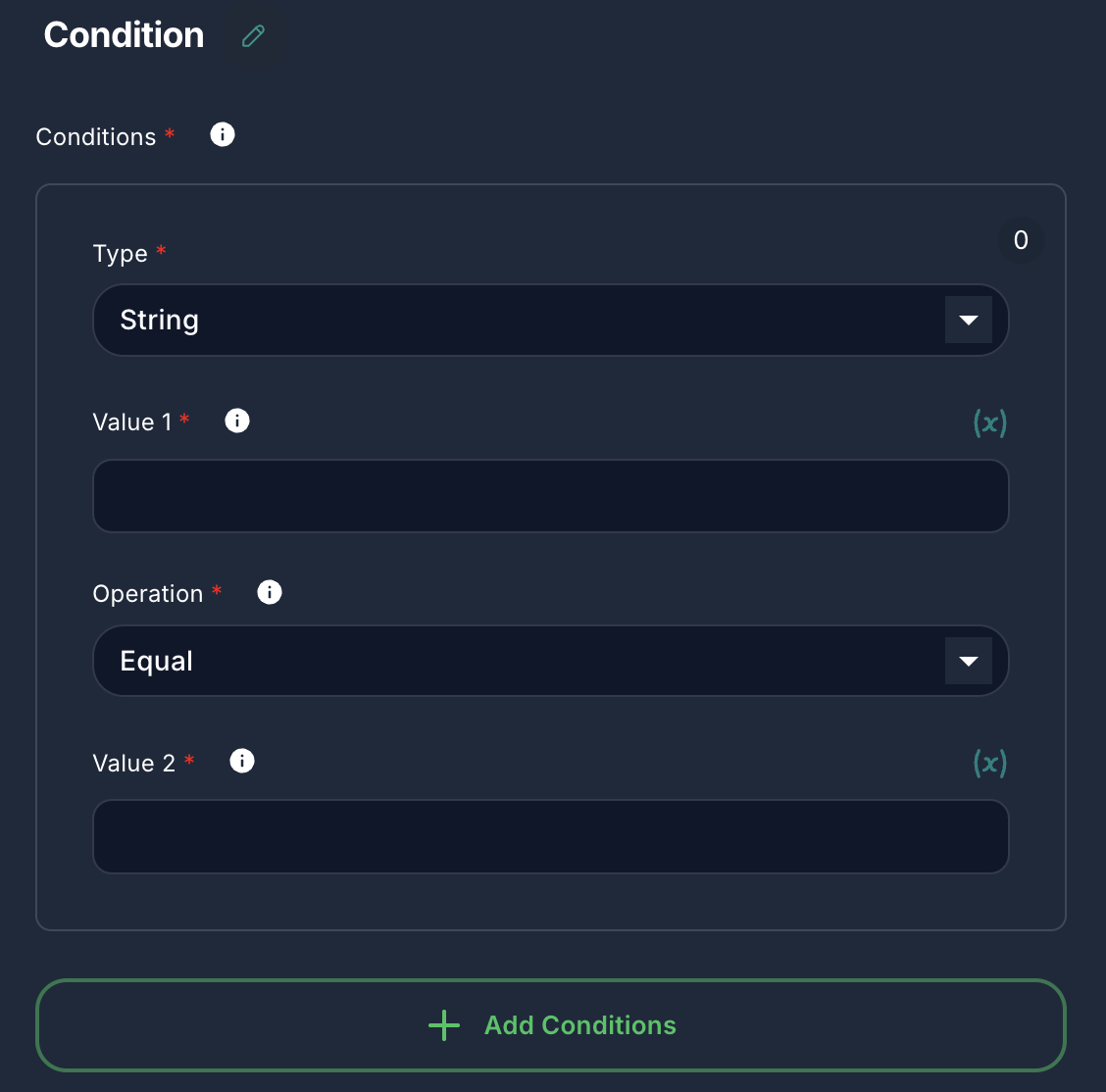
Common Properties for all Types:
- Type:
- Label: Type
- Type:
options - Default:
string - Options:
String,Number,Boolean - Description: Specifies the data type of the values being compared. This affects the available operations and how values are interpreted.
String Comparison:
- Value 1:
- Label: Value 1
- Type:
string - Description: The first string value to be compared. Supports variables.
- Operation:
- Label: Operation
- Type:
options - Default:
equal - Options:
Contains,Ends With,Equal,Not Contains,Not Equal,Regex,Starts With,Is Empty,Not Empty - Description: The type of comparison to perform on string values.
- Value 2:
- Label: Value 2
- Type:
string - Description: The second string value to be compared. Supports variables. (Hidden for
Is EmptyandNot Emptyoperations).
Number Comparison:
- Value 1:
- Label: Value 1
- Type:
number - Description: The first numeric value to be compared. Supports variables.
- Operation:
- Label: Operation
- Type:
options - Default:
equal - Options:
Smaller,Smaller Equal,Equal,Not Equal,Larger,Larger Equal,Is Empty,Not Empty - Description: The type of comparison to perform on numeric values.
- Value 2:
- Label: Value 2
- Type:
number - Default:
0 - Description: The second numeric value to be compared. Supports variables.
Boolean Comparison:
- Value 1:
- Label: Value 1
- Type:
boolean - Default:
false - Description: The first boolean value to be compared.
- Operation:
- Label: Operation
- Type:
options - Default:
equal - Options:
Equal,Not Equal - Description: The type of comparison to perform on boolean values.
- Value 2:
- Label: Value 2
- Type:
boolean - Default:
false - Description: The second boolean value to be compared.
Inputs & Outputs
- Input: The Condition node typically receives an input that contains the data to be evaluated (e.g., a user's message, a variable from a previous node).
- Outputs: The node has multiple output ports:
0(Condition 0): This is the output path taken if the first condition in theConditionsarray is met.1(Else): This is the default output path taken if none of the defined conditions are met.- Additional numbered outputs (
2,3, etc.) will appear for each subsequent condition you add in theConditionsarray.
Example Usage: Routing based on User Intent
Imagine you want to route a user's query to different sub-workflows based on keywords in their message.
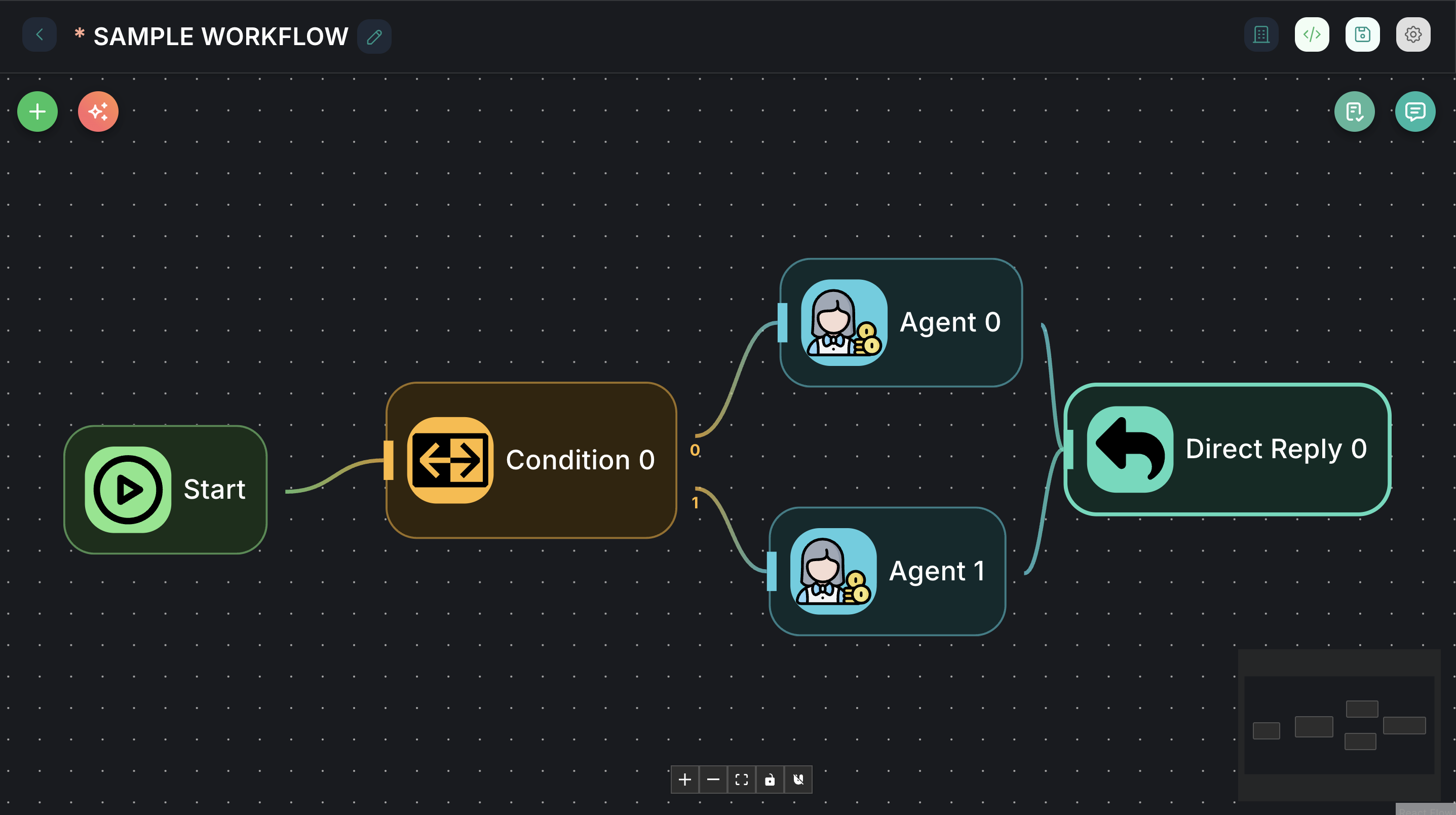
-
Connect a
Startnode to the input of aConditionnode.
-
Configure Conditions:
-
Condition 0:
- Type:
String - Value 1:
{{input}}(assuming user input is passed asinputvariable) - Operation:
Contains - Value 2:
support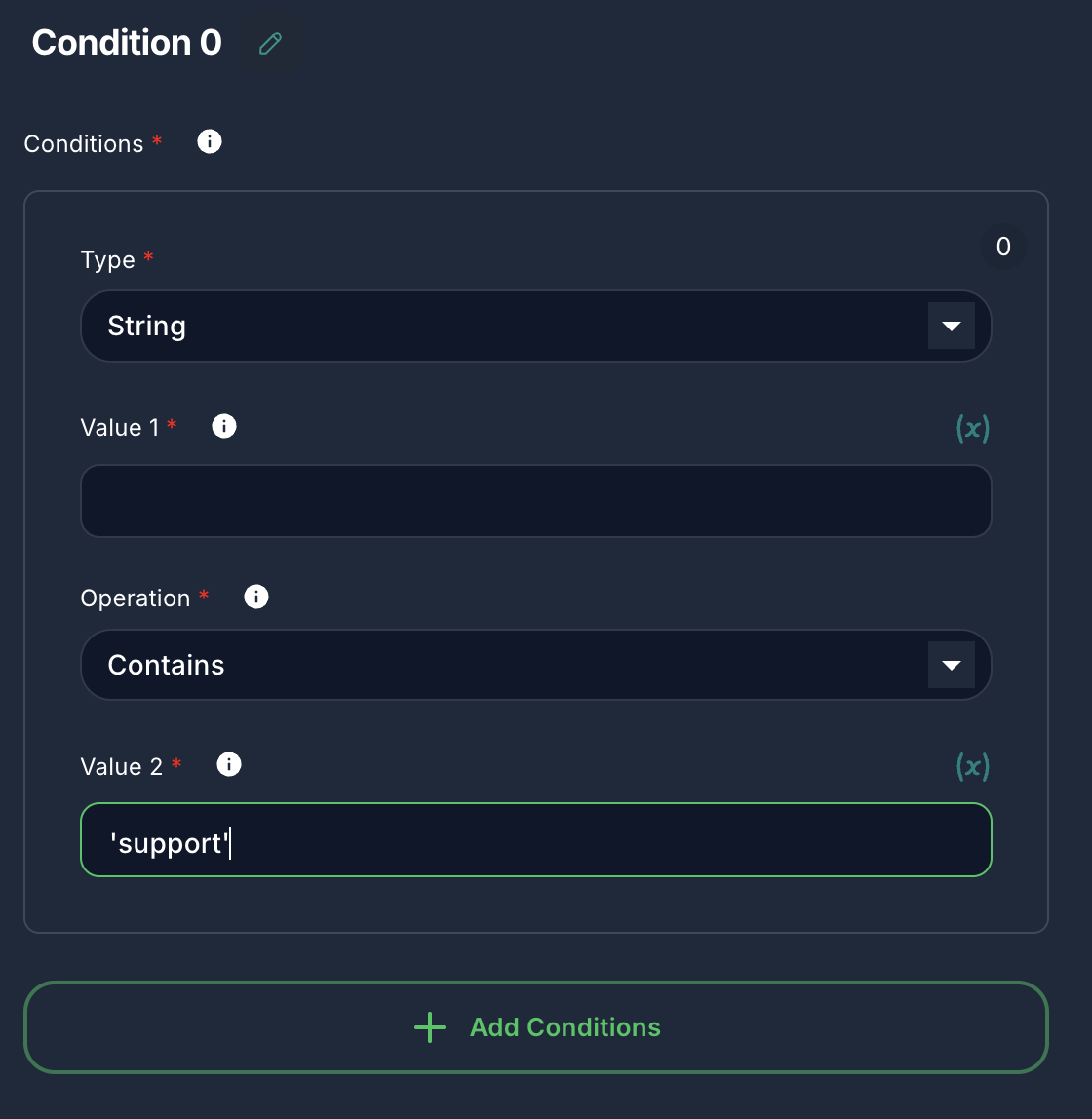
- Type:
-
Condition 1:
- Type:
String - Value 1:
{{input}} - Operation:
Contains - Value 2:
sales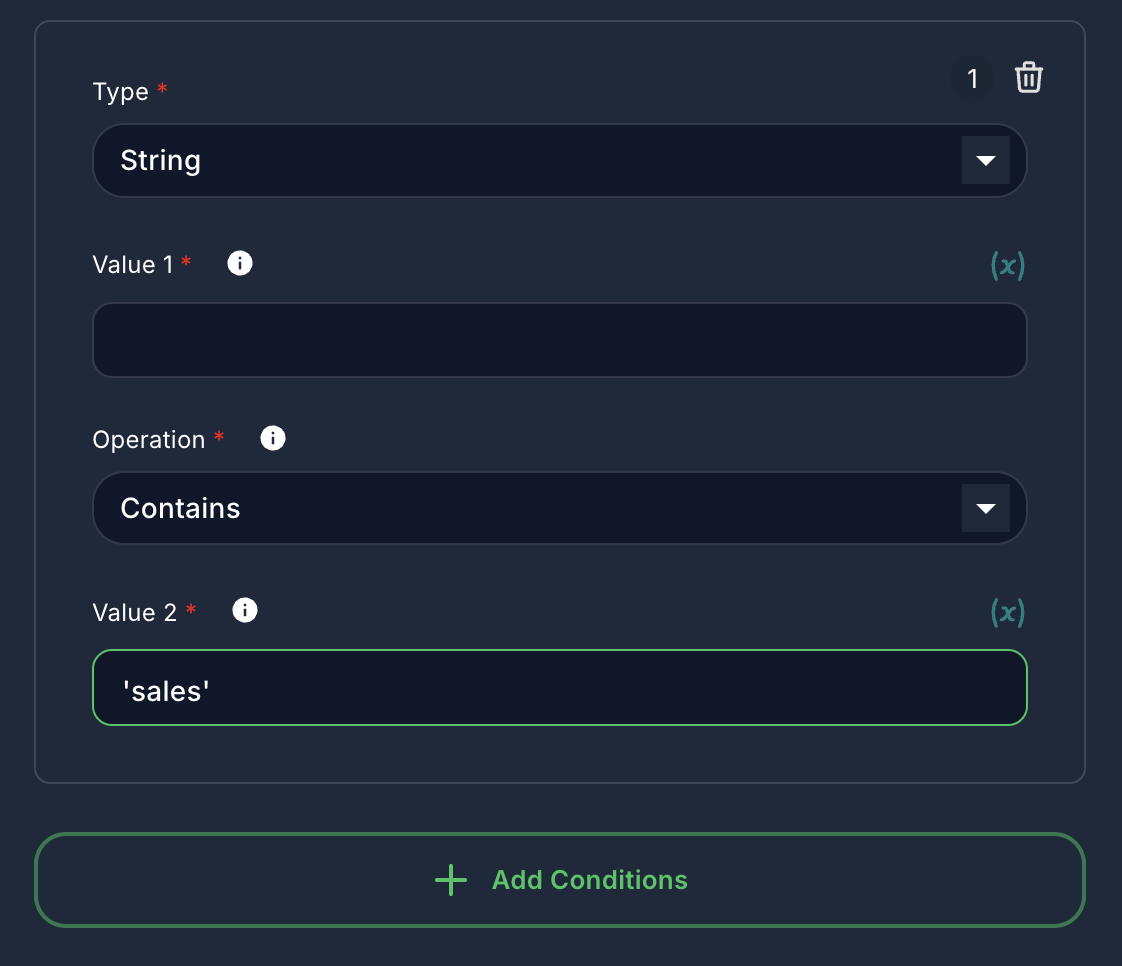
- Type:
-
-
Connect Outputs:
- Connect the
0output of the Condition node to a "Customer Support Chatflow" node. - Connect the
1output of the Condition node to a "Sales Inquiry Chatflow" node. - Connect the
Elseoutput (which will be2in this case) to a "General Inquiry Chatflow" node.
- Connect the
Now, if the user's message contains "support," it goes to customer support. If it contains "sales," it goes to sales. Otherwise, it goes to general inquiry.