Agent
Learn about agent and how to implement it effectively.
Agent (Agentflow Node)
The Agent node within Agentflow is a powerful component that enables your AI workflows to dynamically choose and utilize tools during runtime, facilitating multi-step reasoning and complex task execution. It acts as the "brain" of your workflow, allowing the AI to observe, think, and act.

Purpose
The Agent node is designed for scenarios where a simple, linear chatflow is insufficient. It empowers the AI to:
- Reason: Understand the user's intent and the current state of the conversation.
- Plan: Determine the best course of action, including which tools to use.
- Act: Execute selected tools to gather information or perform actions.
- Iterate: Continuously refine its understanding and actions based on tool outputs.
Appearance on Canvas
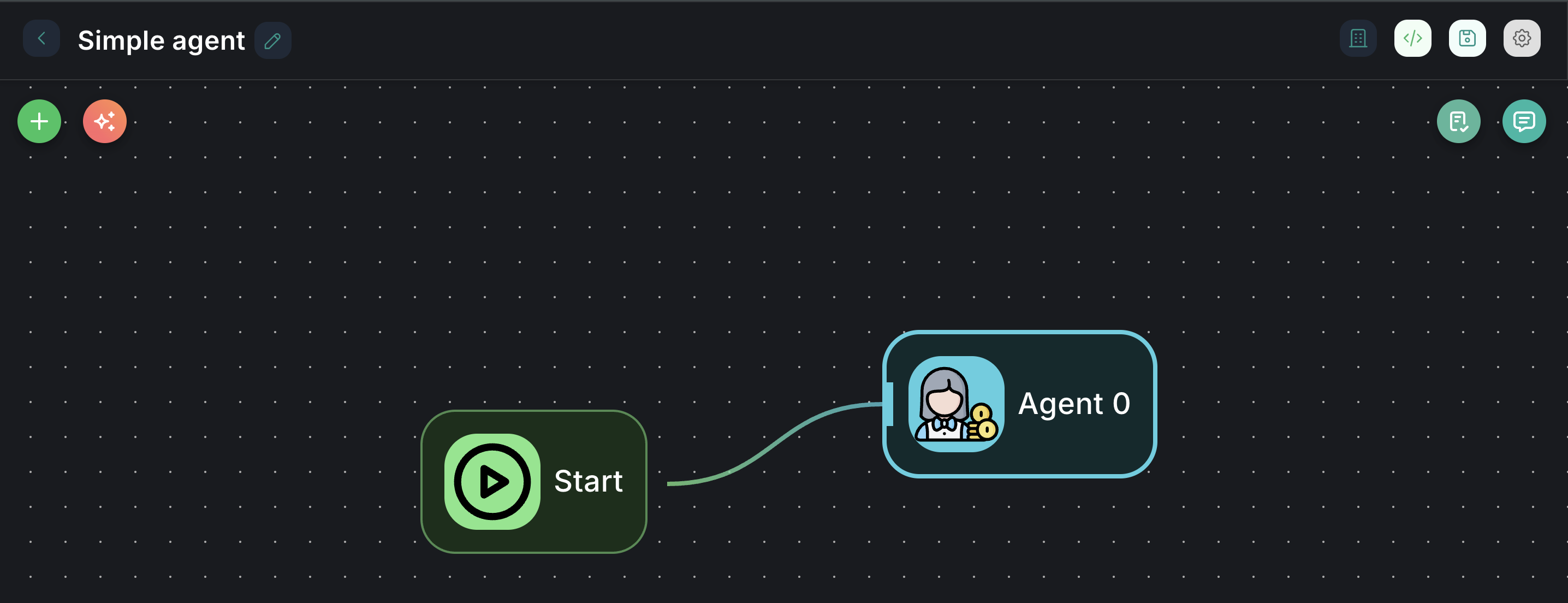
Configuration Parameters
The Agent node offers extensive configuration options to tailor its behavior:
1. Model (Required)
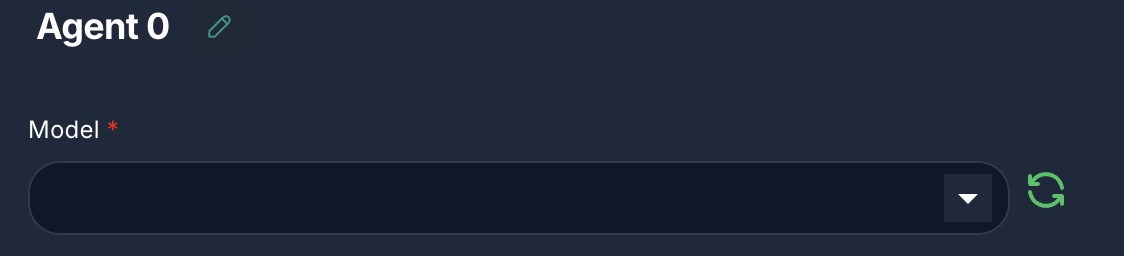
- Label: Model
- Type:
asyncOptions(loads available Chat Models) - Description: Select the Large Language Model (LLM) that will serve as the agent's reasoning engine. This LLM will make decisions on tool usage and response generation.
- Configuration: You can configure the selected model's specific parameters (e.g., API key, temperature, model name) via the
agentModelConfigproperty, which is loaded dynamically.
2. Messages (Optional)
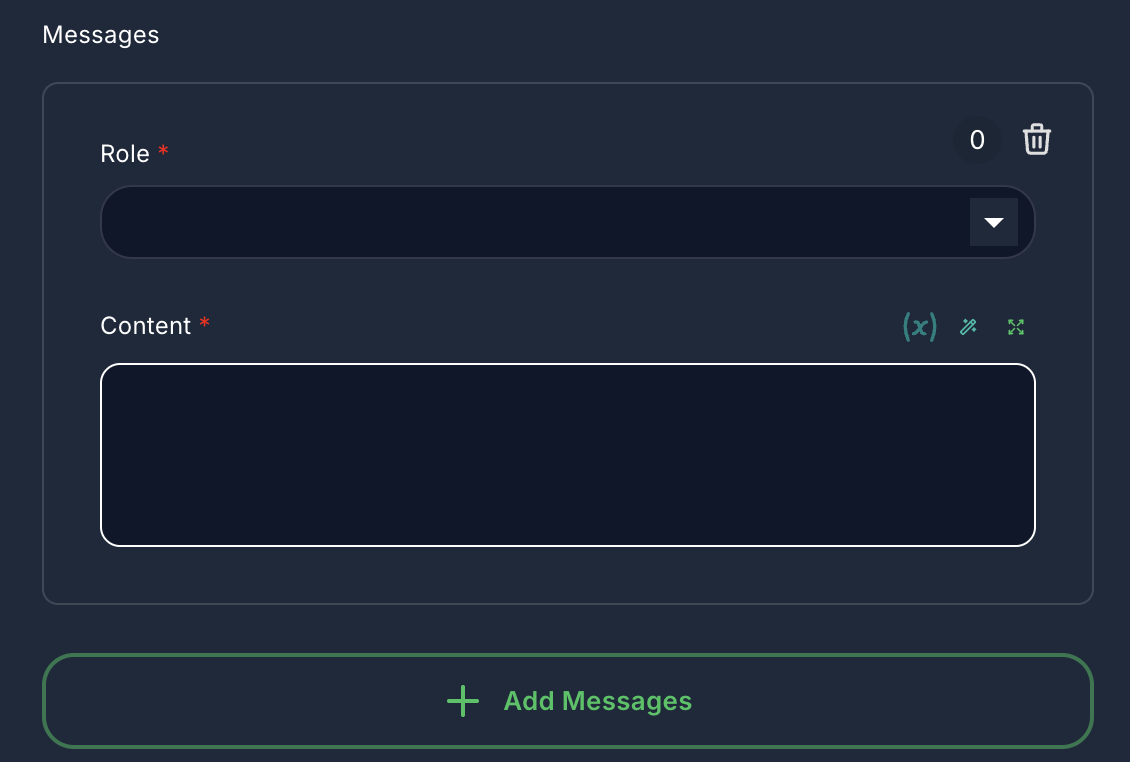
- Label: Messages
- Type:
arrayof objects - Description: Pre-define a series of messages (System, Assistant, Developer, User) to set the context or persona for the agent. These messages are prepended to the conversation history.
- Role:
system,assistant,developer,user - Content: The message text. Supports variables.
- Role:
3. Tools (Optional)
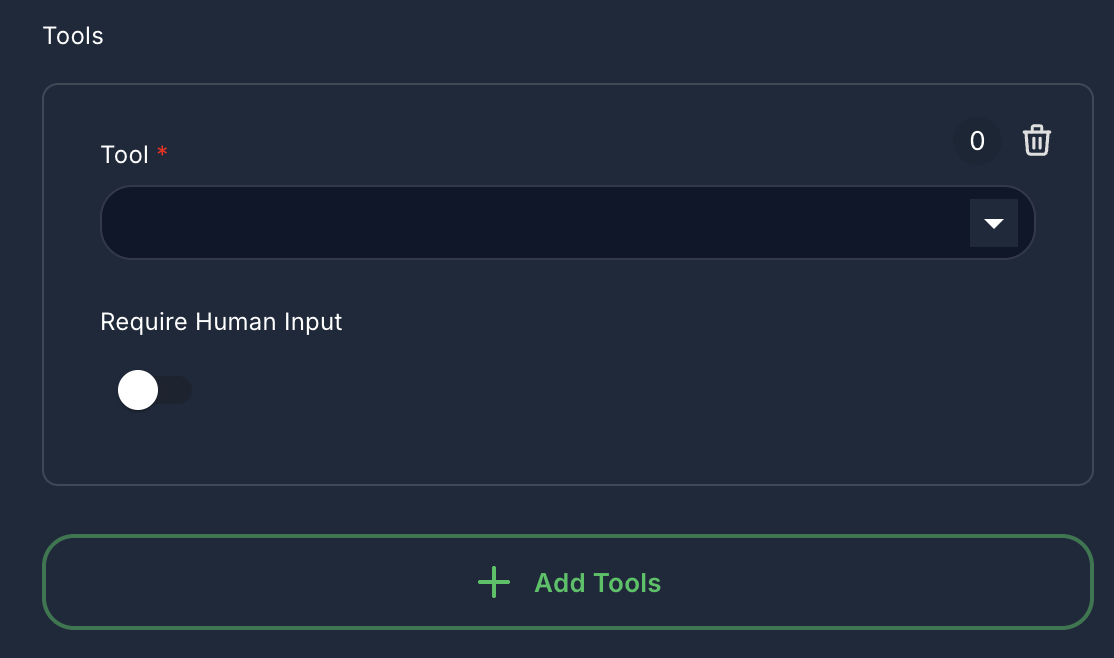
- Label: Tools
- Type:
arrayof objects - Description: Provide the agent with a set of external tools it can use. The agent will decide which tool to invoke based on its reasoning.
- Tool: Select an available tool component (e.g., Google Search, Database Query).
- Require Human Input: If
true, the agent will pause and request human confirmation before executing this tool.
4. Knowledge (Document Stores) (Optional)
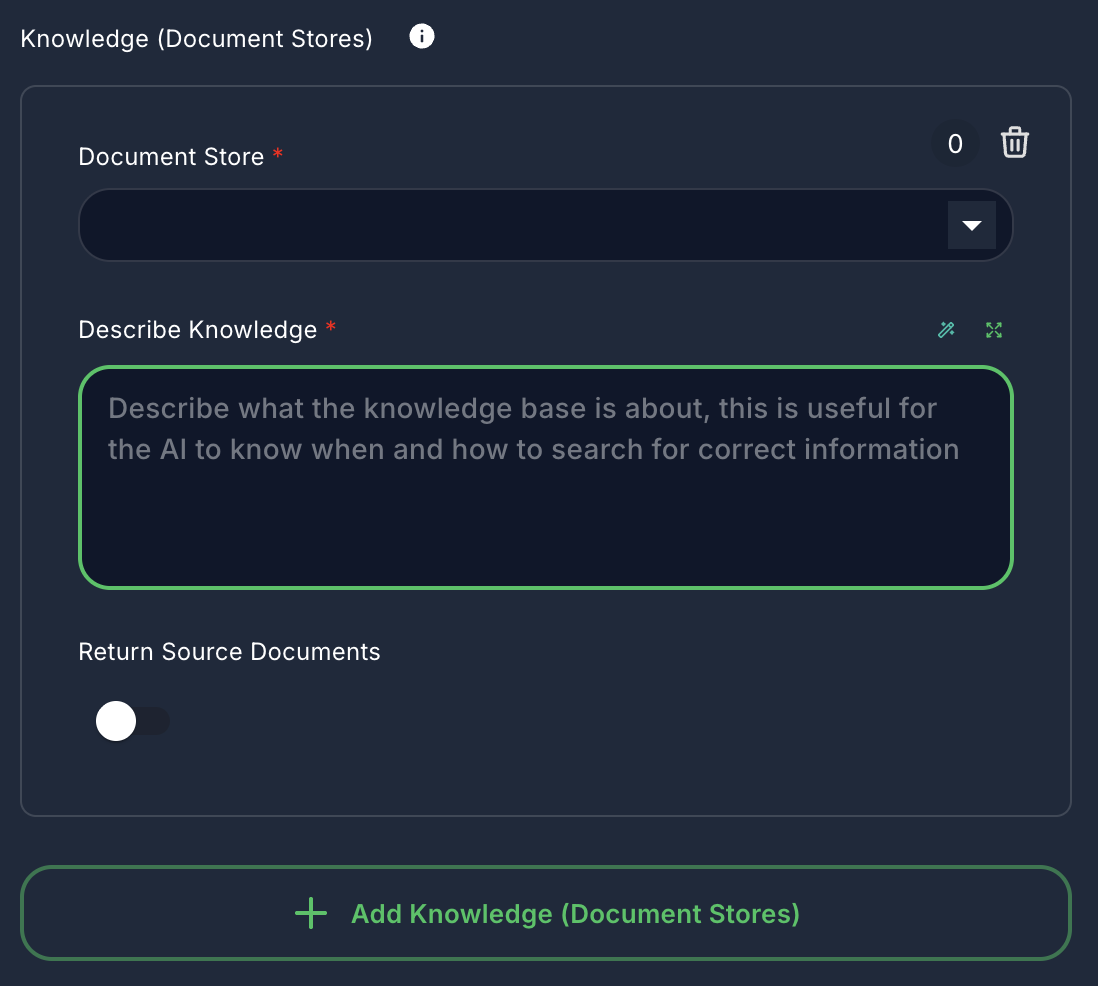
- Label: Knowledge (Document Stores)
- Type:
arrayof objects - Description: Give your agent access to information stored in existing Document Stores. The agent can query these stores to retrieve relevant documents.
- Document Store: Select an upserted Document Store.
- Describe Knowledge: A description of what the knowledge base is about, helping the AI decide when and how to search it.
- Return Source Documents: If
true, the original source documents retrieved will be included in the output.
5. Knowledge (Vector Embeddings) (Optional)
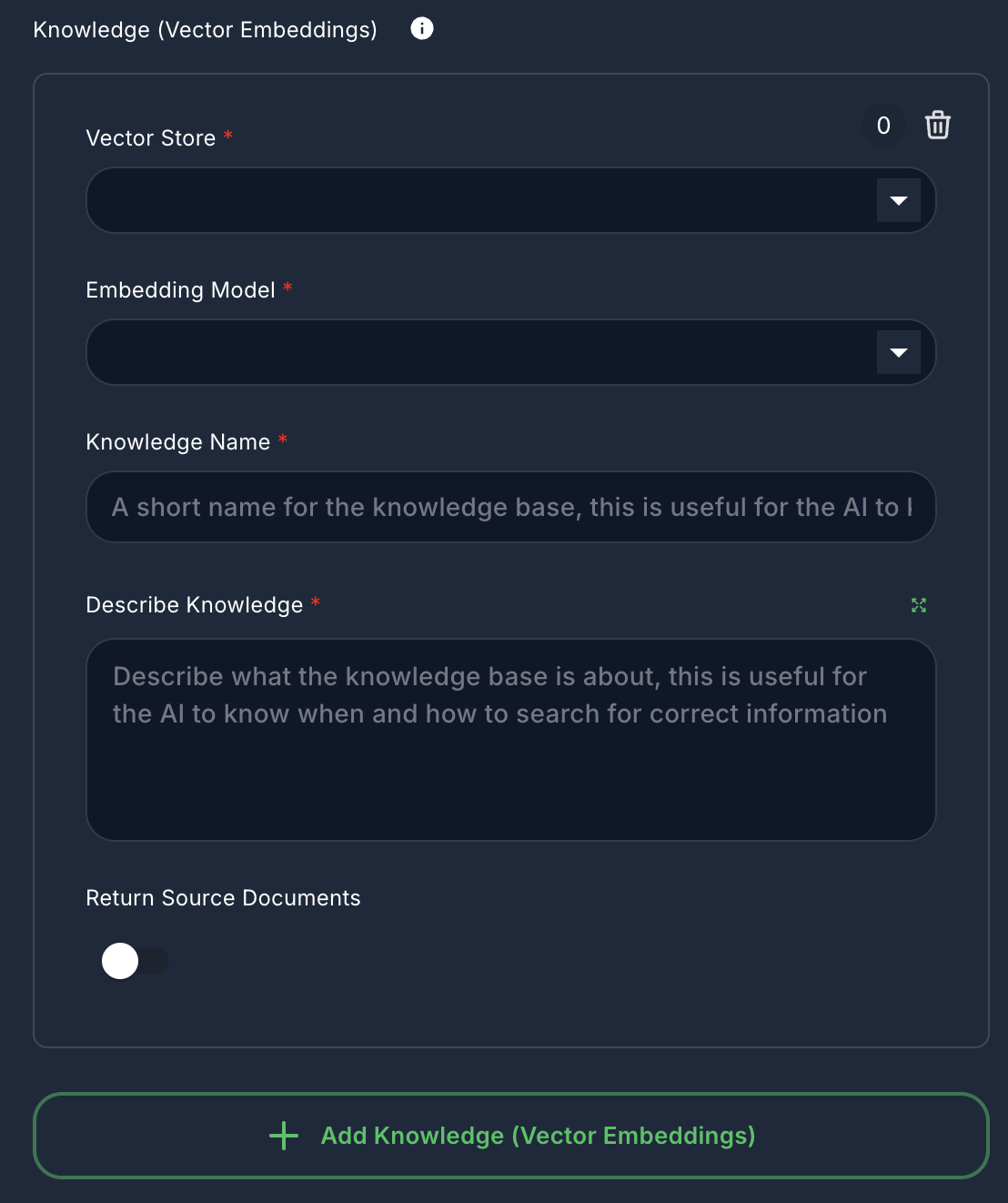
- Label: Knowledge (Vector Embeddings)
- Type:
arrayof objects - Description: Provide the agent with context from existing Vector Stores and Embedding Models. This is used for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
- Vector Store: Select an existing Vector Store.
- Embedding Model: Select an Embedding Model to generate embeddings for queries.
- Knowledge Name: A short name for this knowledge base.
- Describe Knowledge: A description of the knowledge base, guiding the AI on its usage.
- Return Source Documents: If
true, the original source documents retrieved will be included in the output.
6. Enable Memory (Optional)
- Label: Enable Memory
- Type:
boolean - Default:
true - Description: If enabled, the agent will maintain conversational memory, allowing it to remember past interactions.
7. Memory Type (Optional)
- Label: Memory Type
- Type:
options - Default:
allMessages - Description: Defines how the agent manages its conversational history.
- All Messages: Retrieves all messages from the conversation.
- Window Size: Uses a fixed window to surface the last N messages.
- Conversation Summary: Summarizes the entire conversation.
- Conversation Summary Buffer: Summarizes conversations once a token limit is reached.
8. Window Size (Optional)
- Label: Window Size
- Type:
number - Default:
20 - Description: (Visible when Memory Type is "Window Size") Specifies the number of recent messages to retain in memory.
9. Max Token Limit (Optional)
- Label: Max Token Limit
- Type:
number - Default:
2000 - Description: (Visible when Memory Type is "Conversation Summary Buffer") The maximum token limit before the conversation is summarized.
10. Input Message (Optional)
- Label: Input Message
- Type:
string - Description: Add an additional input message as a user message at the end of the conversation. Useful for dynamic inputs.
11. Return Response As
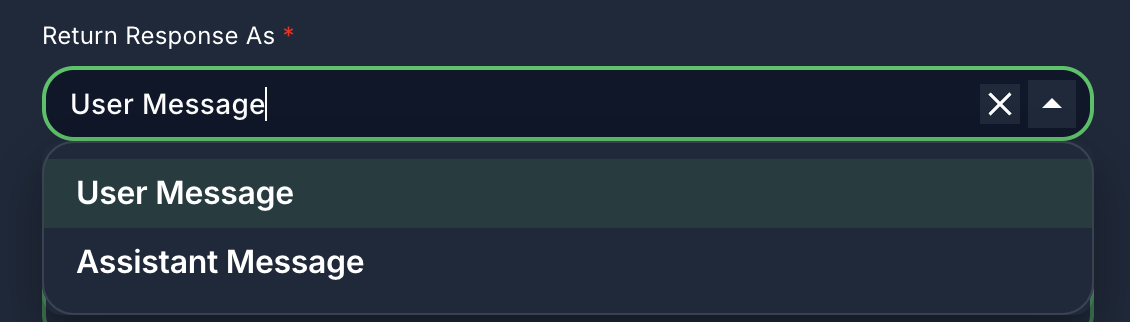
- Label: Return Response As
- Type:
options - Default:
userMessage - Description: Determines how the agent's final response is formatted in the output.
- User Message: The response is treated as if it came from a user.
- Assistant Message: The response is treated as if it came from an assistant.
12. Update Flow State (Optional)
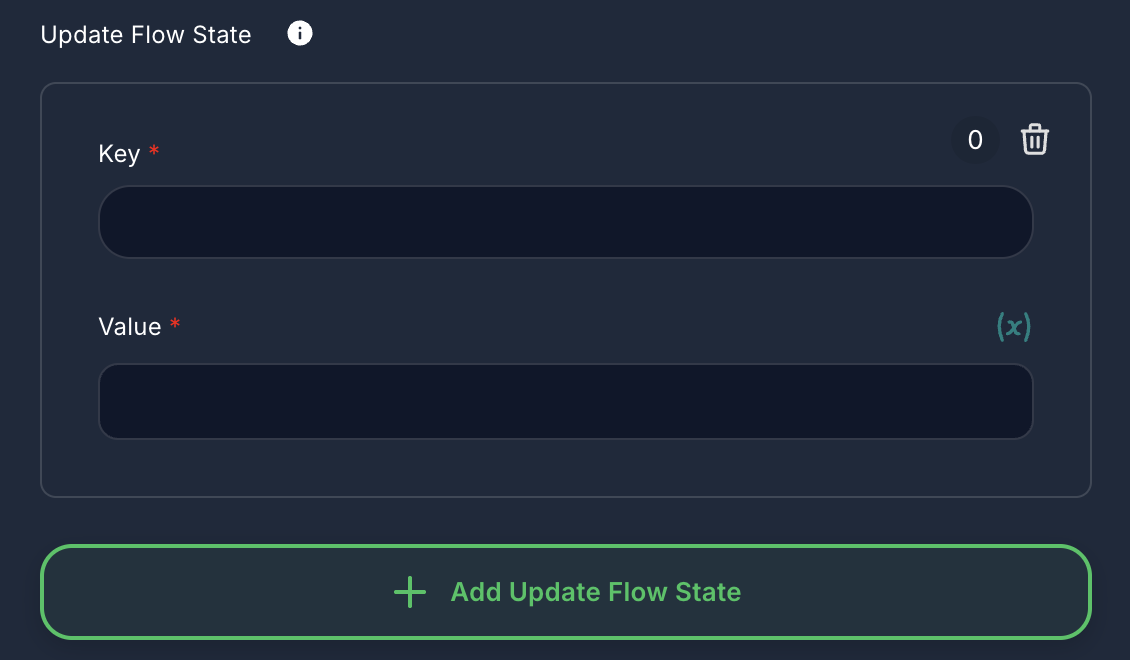
- Label: Update Flow State
- Type:
arrayof objects - Description: Allows you to update the runtime state of the workflow during the agent's execution.
- Key: The key of the state variable to update.
- Value: The new value for the state variable. Supports variables and node outputs.
Inputs & Outputs
- Input: Typically receives a user message or a structured input from a preceding node.
- Output: Produces the agent's response, which can be a text message, a tool call, or a structured output. It also includes metadata like
usedTools,sourceDocuments,artifacts, andusageMetadata.
Example Usage
A common use case for the Agent node is to create a dynamic assistant that can answer questions by searching the internet.

- Drag an
Agentnode onto the canvas. - Configure Model: Select an
OpenAI Chat Model(or similar LLM) and provide its credentials. - Add Tool: In the "Tools" section, add a
Google Searchtool. - Enable Memory: Keep "Enable Memory" checked.
- Connect to Chat Output: Connect the output of the
Agentnode to aChat Outputnode.
Now, when you interact with this chatflow, the agent will use its LLM to decide if it needs to use the Google Search tool to answer your questions.